In this blog, we will understand what is SSL/TLS and how it helps in securing the communication between a client and a server over the internet. Also, the difference between HTTP and HTTPS. Let’s start with the question, “What is SSL?”.
What is SSL/TLS?
SSL stands for Secure Sockets Layer and is mainly used to secure any type of communication over the Internet.
SSL is an older technology that has some security flaws. TLS which stands for Transport Layer Security, is the upgraded version of SSL that fixes existing SSL vulnerabilities. SSL was deprecated in 1999, but we still use the terms SSL and TLS interchangeably.
Purpose of using SSL/TLS
HTTP is a well-known protocol which we all know is used for client-server communication over the Internet. HTTP by itself is unsecured, SSL/TLS protocol on an unsecured HTTP connection makes it secure which is called HTTPS (secured HTTP).
In simpler terms, without HTTPS all the communication between a client and a server is done using plain text. This simply means that any data for example username, password, credit card information etc., and any data which is exchanged between the client and the server over HTTP will be done using plain text. Anybody who has the ability to intercept the communication between the client and the server can read the data easily and misuse this information.
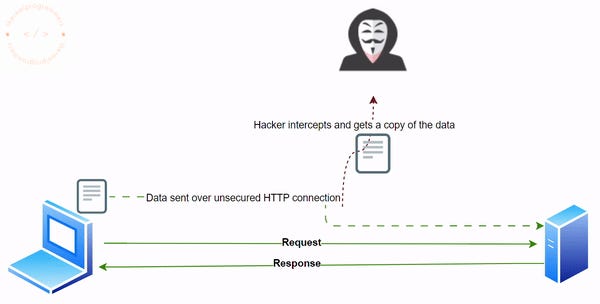
HTTP extended with SSL/TLS is called HTTPS. HTTPS enables encryption of any data which is used during the communication between the client and the server. In this way, if the communication is intercepted in the middle by a hacker they will just receive some encrypted data which is of no use to them.
How does SSL/TLS work?
- To establish a secured connection, the process starts with a process called TLS handshake in which a public key is exchanged for secured communication.
- Both the client and the server generate session keys during the TLS handshake, this session key encrypts and decrypts all the communication afterwards.
- TLS also authenticates the identity of the server, or the website using the server’s TLS certificate.
- TLS also ensures the integrity of the data using a message authentication code (MAC) which is generated using the session keys and included with each message/data transmitted to the client/server.
What happens in a TLS handshake?
As mentioned earlier the TLS/SSL process starts with a TLS handshake. We will now go into details to understand what happens in a TLS/SSL handshake.
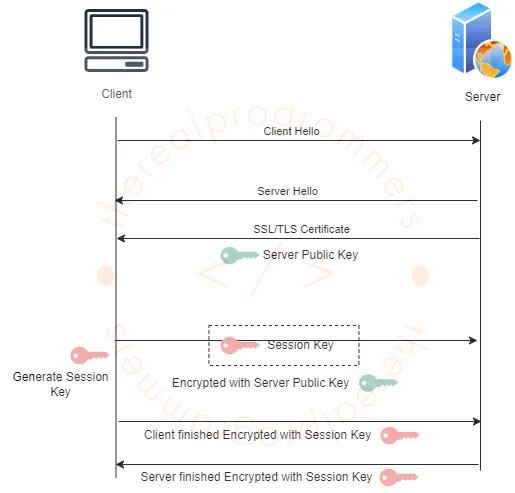
- The client sends a hello message to the server called “Client Hello”. The client here is the users’ browsers. This also includes the supported TLS version and the cipher suites (the algorithm used for encryption) that the client supports for encrypting the data.
- The server responds with its own hello message called “Server Hello”. Also, select the TLS version and cipher suites based on the client’s suggestions.
- Then the server sends its SSL/TLS certificate which also contains its public key. This certificate is used by the client to verify the authenticity of the server with the certificate authority who issued it and the public key is used to encrypt the session key.
- The client generates a session key then encrypts it with the server’s public key and sends it to the server.
- Thus a secured connection is established and the same session key is used to encrypt and decrypt messages at the client and server until the end of the session.
This is how the SSL/TLS works and secures the communication between a server and a client.
Hope you liked this post.


Leave a comment